Microsoft word - v9n3udoag
Comparison of the antibacterial activities of different brands of Ciprofloxacin
Comparación de la actividad antibacterial de diferentes marcas de Ciprofloxacina
Muhammad Shahid NAZIR MUGHAL , Muhammad Tahir ASGHAR, Muhammad Atif ZIA
and Tariq ISMAIL
Pharmaceutical Lab, Punjab Institute of Paramedical Studies. 13 Mamdot Block Mustafa Town Lahore Pakistan.
E-mail:
[email protected] Corresponding author
Received: 02/23/2009
First reviewing ending: 05/12/2009
First review received: 09/01/2009
Accepted: 09/02/2009
ABSTRACT
The present study was carried out to evaluate and compare the antibacterial susceptibility of Gram-positive and Gram-
negative bacteria to Cyrocin (Ciprofloxacin). The following three bacterial strains were used:
Staphyloccocus aureus
[ATCC 25923],
Escherichia coli [ATCC 25922] and
Pseudomonas aeruginosae [ATCC 27853]. Standard commercial discs
of definite potency are used as reference standard (Ciprofloxacin 5g [CTO425B - OXOID Ltd. UK]). The test products
were 250 mg and 500 mg tablets of the following brands: Cyrocin (Highnoon Laboratories Limited), Ciproxin (Bayer
Pharma (Pvt) Ltd. – Pakistan), Mercip (Merck Marker (Pvt.) Ltd., Pakistan) and Axcin (Sandoz - Norvatis Pharma Ltd.,
Pakistan). The media used were: Nutrient Broth (Cat. No. 1.05443, Merck, Germany) and Mueller Hinton Agar [Oxoid].
The study showed no statistically significant difference in the results of different brands.
Kew words: Antibacterial properties,
Staphyloccocus aureus,
Escherichia coli,
Pseudomonas aeruginosae, Ciprofloxacin
El presente estudio se realizó para evaluar y comparar la susceptibilidad antibacterial de las bacterias Gram-positiva y
Gram-negativa al Cyrocin (Ciprofloxacina). Se usaron las cepas bacetriales
Staphyloccocus aureus [ATCC 25923],
Escherichia coli [ATCC 25922] y
Pseudomonas aeruginosae [ATCC 27853]. Se utilizaron discos comerciales estandars de
potencia definida como estandar de referencia (Ciprofloxacin 5g [CTO425B - OXOID Ltd. UK]). Los productos
evaluadoes fueron tabletas de 250 mg y 500 mg de las siguientes marcas: Cyrocin (Highnoon Laboratories Limited),
Ciproxin (Bayer Pharma (Pvt) Ltd. – Pakistan), Mercip (Merck Marker (Pvt.) Ltd., Pakistan) y Axcin (Sandoz - Norvatis
Pharma Ltd., Pakistan). Los medios usados fueron: Nutrient Broth (Cat. No. 1.05443, Merck, Germany) and Mueller Hinton
Agar [Oxoid]. El estudio mostró diferencias estadísticamente no significativas en los resultados de las diferentes marcas,
Palabras clave: Propiedades antibacteriales,
Staphyloccocus aureus,
Escherichia coli,
Pseudomonas aeruginosae,
testing. In this method, the paper discs impregnated
with a defined quantity of antimicrobial agent are
Antimicrobial susceptibility tests measure the
placed on agar medium uniformly seeded with test
ability of an antibiotic or other antimicrobial agents
organism. A concentration gradient of the antibiotic
under suitable conditions to inhibit bacterial growth
in
forms by diffusion from the disc and growth of test
vitro (Inhibitory effect on micro-organism) (Bauer
et
organism is inhibited at a distance from the disc that
al. 1966).
is related among other factors to the susceptibility of
For evaluating the safety and effectiveness of
antibiotic products, several types of antimicrobial
The modified "Kirby Bauer Method" is the
susceptibility (sensitivity) tests are recommended.
recommended method by National Committee on
The choice of the method depends on local needs and
Clinical Laboratory Services (NCCLS-USA)
resources, however, the disk diffusion test has a long
subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility testing
and successful track record; it is still the most
(Bauer
et al. 1966). The Bauer Kirby procedure has
common test used for antimicrobial susceptibility
been standardized to correlate the zone diameter
Revista UDO Agrícola 9 (3): 700-704. 2009
Nazir Mughal
et al. Comparison of the antibacterial activities of different brands of Ciprofloxacin
produced by the fixed amount of antimicrobial agent
1990). They may also interact with the GABA A
in the disc with an MIC for the drug–organism
receptor and cause neurological symptoms; this is
combination. The results may be interpreted as further augmented by certain non-steroidal anti-resistant, intermediate, moderately susceptible or inflammatory drugs (Krishek and Smart, 2001). susceptible. The term intermediate is important. It
generally means that the result is inconclusive for that
The present study was carried out to evaluate
drug-organism combination. The term moderately
and compare the antibacterial susceptibility of Gram-
susceptible is applied to those situations where a drug
positive (
Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative
may be used for infections in a particular body site,
(
Escherichia-coli and
Pseudomonas aeruginosae)
e.g. cystitis, because it is highly concentrated in the
bacterial strains to Cyrocin (Ciprofloxacins) 250 mg
urine. The interpretive standards for Ciprofloxacin 5
and 500 mg tablets of Highnoon Laboratories and
µg disc are given by National committee for clinical
three other leading brands of the same drug.
laboratory standards is: Resitatant 15; Intermediate
16-20 y Susceptible 21.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro®) was discovered in
Test organisms
1960s by Bayer. Its discovery stemmed from
researchers in the 1960s looking for an alternative
The following three bacterial strains were
treatment to malaria. Cipro® was approved in 1987
used for the study:
by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a broad-
spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-
Staphyloccocus aureus
[ATCC 25923]
positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Since then it has
Escherichia coli
[ATCC 25922]
been prescribed to over 500 million patients
Pseudomonas aeruginosae
[ATCC 27853]
worldwide. Cipro® has been approved for the
treatment of 14 types of infection including
Reference standard
respiratory and urinary tract infections, skin, and
other gastro-intestinal infections (SIS, 1987). Cipro®
Standard commercial discs of definite
is the most widely used fluoroquinolone antibiotic in
potency are used as reference standard (Ciprofloxacin
the world, which testifies to its wide range of uses. It
5g [CTO425B - OXOID Ltd. UK])
is also the first antibiotic to be approved specifically
for an indication associated with the intentional use of
Test products
a lethal biological weapon (Hilliard
et al. 1995).
Cipro is available in three different forms: Tablets,
The 250 mg and 500 mg tablets of the
Oral Suspension (strawberry-flavored liquid to be
following brands were tested: Cyrocin (Highnoon
taken by mouth), and I.V. (which a doctor or nurse
Laboratories Limited), Ciproxin (Bayer Pharma (Pvt)
injects directly into the bloodstream) (Drusano
et al.
Ltd. – Pakistan), Mercip Merck Marker (Pvt.) Ltd.,
Pakistan) and Axcin (Sandoz - Norvatis Pharma Ltd.,
Pakistan).
Because of its general safety, potency and
broad spectrum activity, Ciprofloxacin was initially
reserved as a "last-resort" drug for use on difficult and
drug-resistant infections. As with any antibiotic,
Nutrient Broth (Cat. No. 1.05443, Merck,
however, increasing time and usage has led to an
Germany) and Mueller Hinton Agar [Oxoid].
increase in Ciprofloxacin-resistant infections, mainly
in the hospital setting. Also, implicated in the rise of
Preparation of Turbidity Standard
resistant bacteria is the use of lower-cost, less potent
fluoroquinolones, and the widespread addition of
The turbidity standard was prepared by
Ciprofloxacin and other antibiotics to the feed of farm
pouring 0.6ml of a 1% (10 g L-1) of solution of
animals, which leads to greater and more rapid weight
Barium chloride dehydrate into a100ml graduated
gain, for reasons which are not clear (Brouwers,
cylinder and making up the volume to 100ml with 1%
1992). The toxicity of drugs that are metabolised by
(10ml/l) sulfuric acid.
the cytochrome P450 system is enhanced by
concomitant use of some quinolones (Janknegt,
Revista UDO Agrícola 9 (3): 700-704. 2009
Nazir Mughal
et al. Comparison of the antibacterial activities of different brands of Ciprofloxacin
Preparation of antimicrobial susceptibility test
Inoculation of plates and application of
Standard discs of Ciprofloxacin (Andrews,
1. The plates were inoculated by dipping a
sterile swab into the
inoculum. The
Ciprofloxacin sensitivity disc (5g) of
excess
inoculum was removed by
OXOID- UK were used as a Reference Standard.
pressing and rotating the swab firmly
against the side of the tube above the
Preparation of test disc
level of the liquid.
Discs (6mm in diameter) were punched out
2. The swab were streaked all over the
from 47 mm Petri Pad (Millipore Corporation, USA)
surface of the medium three times
and placed in Petri dishes allowing a distance of 2-4
rotating the plates through an angle of
mm between each disc and sterilized in a hot air oven
60 after each application. Finally, the
at 160C for 1 hour.
swab was passed around the edge of the
agar surface. The agar was left to dry for
The average weight of five tablets was taken
a few minutes at room temperature with
and the tablets were ground and the powder
the lid closed. The antibiotic discs were
equivalent to 50 mg was taken in a 100mL volumetric
placed on the inoculated plates using a
flask. Added 15-20 mL distilled water into the flask
sterile forceps.
and sonicated for few minutes and made up the
volume upto the mark. An aliquot of 0.01mL (10L)
3. The plates were placed in an incubator at
was pipetted onto a separate disc incubated at 37C
35C within 30 minutes of preparation in
for 1 hour placed in labeled air tight container and
a CO2 free atmosphere.
kept in refrigerator at 4C until use.
4. After overnight incubation, the diameter
Procedure for inoculation of plates and application
of each zone was measured and recorded
of plates (The Modified Kirby Bauer Method)
(Barry
et al. 1980).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The inoculum is prepared and disc is applied
as per following procedure:
The study was conducted to compare the
antibacterial susceptibility of Highnoon brands of
Inoculum Preparation
Ciprofloxacin (
i.e. Cyrocin) 250 mg and 500 mg
tablets with the pure Ciprofloxacin (as standard) and
1. To prepare the
inoculum from culture
three other leading brands of Ciprofloxacin tablets of
plate, touch with a loop the tops of each
3.5 colonies of similar appearance of the
organism to be tested.
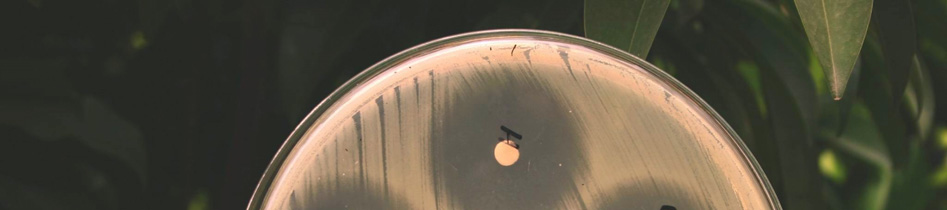
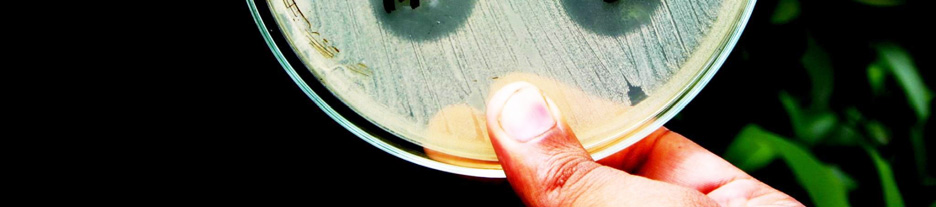
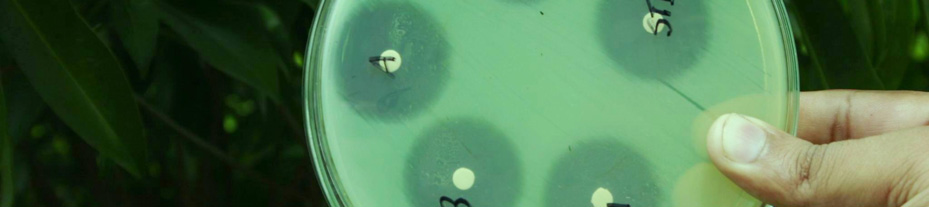
The results of the study in terms of inhibition
zone diameters produced by the 5 g potency discs
2. To make the
inoculum from a pure are given in tables 1 and 2. Also, the photograph of
culture, a loopful of confluent growth is
the plates with the zone of inhibition of different
similarly suspended in saline.
brands of Ciprofloxacin tablets against the tested
bacterial strains is given in figure 1.
3. Compare the tube with turbidity standard
and adjust the density of the test
The comparison of the results with the
suspension to that of the standard by
NLCCS Control limits for monitoring inhibitory zone
adding more bacteria or more sterile
diameters (mm) shows that all the results fall within
saline. Proper adjustment to the turbidity
the acceptance range (NCCLS, 1994). The control
of the
inoculum is essential to ensure that
limits for monitoring inhibitory zone diameter with 5
the resulting lawn growth is confluent or
g disc content of Ciprofloxacin for the bacterial
almost confluent.
strains is given below:
Revista UDO Agrícola 9 (3): 700-704. 2009
Nazir Mughal
et al. Comparison of the antibacterial activities of different brands of Ciprofloxacin
Escherichia coli (ATCC25922): 30-40mm
Apparantly, all the results are comparable and
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC25923): 22-30mm
are similar than standard. Also, the results of Ciproxin
Pseudomonas aeruginosae (ATCC27853): 25-33mm
[Bayer] showed the most consistent zones of
inhibition against three studied bacterial strains
The results for 250 mg tablets were median
followed by Mercip [Merck], Axcin [Sandoz] and
whereas the results for 500 mg tabs fall within the
Cyrocin [Highnoon].
Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of different brands of Ciprofloxacin 250 mg tablets
Zone of Inhibition (mm)
Bacterial Strains
Standard Axcin Ciproxin Cyrocin
35.65 35.15 34.90
Escherichia coli
35.15 34.85 34.40
[ATCC # 25922]
34.70 34.65 34.70
Avg. 34.17 35.16 35.17 34.88 34.67
STDEV 0.68 0.24 0.48
26.07 25.80 25.13
Staphylococcus Aureus
25.45 25.30 24.80
26.10 25.95 25.30
Avg. 24.81 25.52 25.87 25.68 25.08
STDEV 0.11 0.63 0.37
29.07 28.28 28.03
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
28.10 27.70 27.40
28.65 27.90 27.75
Avg.: Average; STDEV: Standard Deviation
Table 2. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of different brands of Ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablets.
Zone of inhibition (mm)
Bacterial Strains
Standard Axcin Ciproxin Cyrocin
35.00 34.20 33.97
Escherichia coli
37.45 33.80 37.99
[ATCC # 25922]
34.47 36.15 34.50
Avg. 33.63 34.81 35.64 34.72 35.49
STDEV 0.53 1.57 1.59
28.77 27.00 27.98
Staphylococcus Aureus
27.32 26.99 26.84
29.00 27.41 27.00
Avg. 27.30 27.20 28.36 27.13 27.27
STDEV 0.61 0.29 0.91
30.03 29.27 29.60
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
32.00 32.00 32.42
32.72 34.68 32.00
Avg.: Average; STDEV: Standard Deviation
Revista UDO Agrícola 9 (3): 700-704. 2009





Nazir Mughal et al. Comparison of the antibacterial activities of different brands of Ciprofloxacin
The statistical analysis revealed that there is
LITERATURE CITED
no significant difference in the results for different
brands and statistically the antibacterial activities of
Andrews, J. M. 2001. BSAC standardized disc
all the brands are similar.
susceptibility testing method. Journal of
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 48, Suppl. S1: 43-57.
Barry, A. L. and C. Thornsberry. 1980. Susceptibility
Testing: Diffusion Test Procedures. In: Lennette, E. H. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 3ª ed., ASM, Washington D. C, U.S.A. p. 464.
Bauer, A. W.; W. M. N. Kirby, J. C. Sherris and M.
Turk. 1966. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45:493-496.
Brouwers, J. R. 1992. Drug interactions with
quinolone antibacterials. Drug Saf 7: 268-281.
Drusano, G. L.; H. C. Standiford, K. Plaisance, A.
Escherichia coli [ATCC #. 25922]
Forrest, J. Leslie and J. Caldwell. 1986. Absolute
oral bioavailability of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 30: 444-446.
Hilliard J. J.; H. M. Krause, J. I. Bernstein, J. A.
Fernandez, V. Nguyen, K. A. Ohemeng and J. F. Barrett. 1995. A comparison of active site binding of 4-quinolones and novel flavone gyrase inhibitors to DNA gyrase. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 390: 59-69.
Janknegt R. 1990. Drug interactions with quinolones.
J. Antimicro. Chemo. 26: 7-29.
Krishek, B. J. and T. G. Smart. 2001. Proton
sensitivity of rat cerebellar granule cell GABAA
Staphylococcus aureus [ATCC #. 25923]
receptors: dependence on neuronal development. J.
Physiol. 530 (2): 219-233.
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory
Standards (NCCLS). 1994. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Proposed Standard. NCCLS document M31-P (ISBN 1-56238-258-6). NCCLS, 771 East Lancaster Avenue, Villanova, PA 19085, USA.
Second Informational Supplement M100-S2. (SIS).
1987. Performance standards for Antimicrobial
Susceptibility Testing. 1987, National Committee
Pseudomonas aeruginosae [ATCC #. 27853]
for clinical laboratory Standards, Villanova, Pa,
Figure 1. Zone of inhibition of different brands of
Ciprofloxacin tablets against the tested bacterial strains.
Revista UDO Agrícola 9 (3): 700-704. 2009
Source: http://udoagricola.orgfree.com/V9N3UDOAg/V9N3Nazir700.pdf
The Effect of the Decontamination of Asthma Spacer Devices on their Function and their Suitability for Reuse in a Paediatric Emergency Abstract Objectives: The aims of this study were to determine the effects of dishwashing and dishwashing frequency on the efficiency of spacer devices used with ipratropium inhalers by determining effects on emitted dose.
ANTIMICROBIAL AND CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY GUIDEBOOK Second edition July 2015 Page 1 of 65 TABLE OF CONTENTS Contacts Clinical Microbiology Organism Identification Flowcharts Antimicrobial Concepts and Tips (future work) Antimicrobial Restrictions and Utilization Guidelines (future work)







